Celiac Disease or Gluten Sensitivity: 9 Signs You are Gluten Intolerant
In the past few decades, more people have begun to notice that consuming bread products which contain gluten have been related to gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, stomach pains, diarrhoea and, in more server cases, vomiting and progressive weight loss. This is, sometimes, due to an autoimmune condition known as celiac disease.
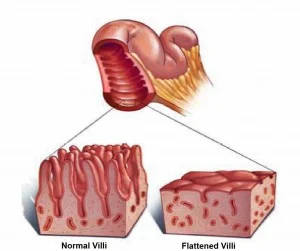
Upon consumption of gluten, those with celiac disease experience a progressive deterioration of the villi, or hair-like projections, within the small intestine. Villi helps to absorb vitamins and nutrients to nourish our bodies and sustain energy for our everyday activities. When this villi begins to flatten as a result of gluten consumption malabsorption can occur, causing anemia, irritability, weight loss, stomach pains and other gastrointestinal complications.
The elimination of all forms of barley, wheat, and rye, even in the smallest amounts (a ‘gluten-free’ diet) is necessary for people with celiac disease. Although there is no cure for this disease, one may adhere to a ‘gluten-free’ diet to slowly reverse damage to the small intestine.
When the test for Celiac is negative, but symptoms improve with a ‘gluten-free’ diet, it is said that someone has gluten sensitivity.
More than 50 diseases have been linked to gluten, the protein found in wheat, rye, and barley. It’s estimated that 99% of the people who have either gluten intolerance or celiac disease are never diagnosed.
Could you be one of them?
If you have any of the following symptoms it could be a sign that you have gluten intolerance:
1. Digestive issues such as gas, bloating, diarrhoea and even constipation.
2. Fatigue, brain fog or feeling tired after eating a meal that contains gluten.
3. Diagnosis of an autoimmune disease such as Rheumatoid arthritis, Ulcerative colitis, Psoriasis, Scleroderma or Multiple sclerosis.
4. Neurologic symptoms such as dizziness or feeling of being off balance.
5. Hormone imbalances
6. Migraine headaches
7. Diagnosis of chronic fatigue or fibromyalgia. These diagnoses simply indicate your conventional doctor cannot pin point the cause of your fatigue or pain.
8. Inflammation, swelling or pain in your joints such as fingers, knees or hips.
9. Mood issues such as anxiety, depression, mood swings, etc.
How to test for gluten intolerance?
I have found the single best way to determine if you have an issue with gluten which is to do an elimination diet out of your diet for at least 3 to 6 weeks and then reintroduce it.
After these 3 – 6 weeks with no gluten, start eating food with gluten; pasta, bread, … Observe and feel what happens over the next twenty-four hours. Notice the following:
- How do you feel immediately after eating it? Are there any sensations in your belly?
- Does anything happened shortly after you eat it, such as a runny nose or mucus in the throat (typical of milk), or fatigue, bloating, or head-ache (typical of wheat)?
- How are you energy levels? A bowl of wheat pasta at night, for instance, may make your feel very tired either immediately after eating it or on waking up the next morning.
- How are your bowel movements the next day?
- How did you sleep that night? Was it a heavier sleep, or were you disturbed?
The best advice that I share with my patients is that if they feel significantly better off of gluten or feel worse when they reintroduce it, then gluten is likely a problem for them. In order to get accurate results from this testing method you must elimination 100% of the gluten from your diet.
How to treat gluten intolerance?
Eliminating gluten 100% from your diet means 100%. Even trace amounts of gluten from cross contamination or medications or supplements can be enough to cause an immune reaction in your body.
If you feel bad, are you still having gluten?